The osteochondrosis of the spine is a disease caused by the destruction of the bone tissues and cartilage of the cervical, thoracic and lumbar column.
First of all, with the progression of the disease, the central part of the spinal disc is modified: the jet core so called. For this reason, the vertebra loses some of its properties that absorb the shocks and refinement and cracks are formed on the fibrous ring along the outskirts of the disc.
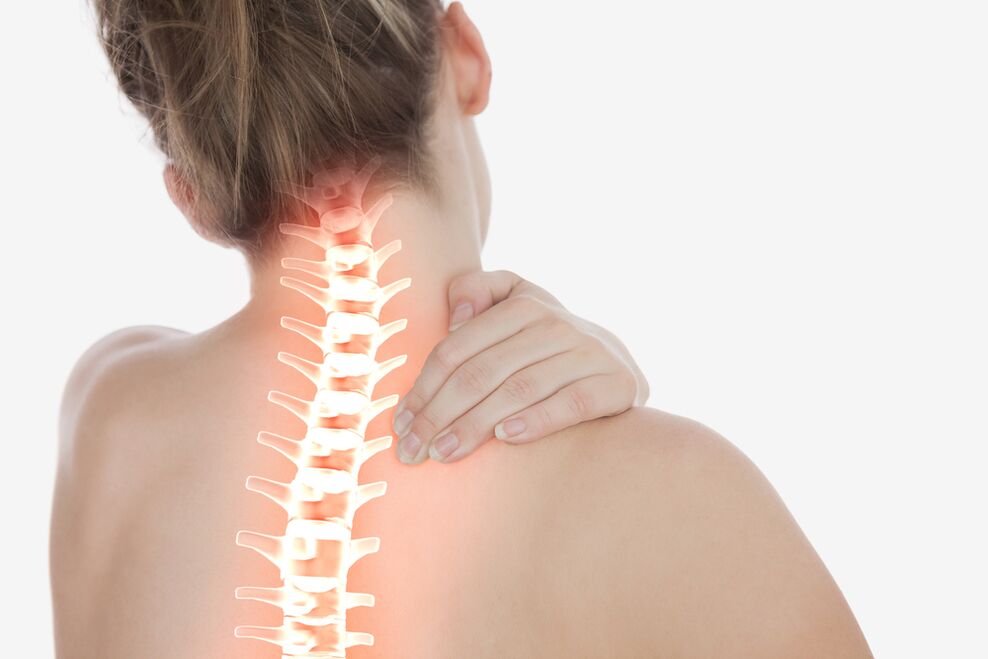
A further progression of the osteocondrosis of the spine leads to complications of the disease: the protrusion of discs or breakage of a fibrous ring and intervertebral hernia, consequently. The instability of the spine in the affected area leads to the pain and limited mobility of the head in the osteochondosis of the cervical column, as well as the limited mobility of the body with osteochondosis of the thoracic and lumbar spine.
In 75% of cases, it is precisely the osteochondosis of the spine which is the cause of back pain. With age, the risk of spinal tissue dystrophy increases significantly, therefore, on average, the symptoms of the osteochondrosis of the spine are observed in every second inhabitant of the planet over the age of 30.
The causes of osteochondosis of the spine
The provocative factors in the development of the osteocondrosis of the spine are considered back or systematic load on the back with hard physical work or a professional employment in vibration conditions. If you have to do a lot of loading and unloading work, buy the hydraulic collection for your car.
The early manifestation of the symptoms of the osteochondrosis of the spine is caused by a weak physical development, flat feet or excess weight. There is also a genetic predisposition to the loose structure of the intervertebral discs and the anomalies of the structure of the spine. Intensive training in the gym in violation of the rules for the distribution of the load on the back, a sedentary lifestyle and an improper diet are also unfavorable in terms of health of the spine.
Symptoms of osteochondosis of the spine
The disease manifests itself as a series of typical symptoms. The osteochondrosis of the spine is characteristic: painful pain in the back, a feeling of numbness in the affected spine, a decrease in the amplitude of the movements, an increase in pain in the lifting of severity, an acute movement, a tension during cough or sneezing.
Chronic pain, as one of the symptoms of osteochondosis of the spine, causes an increase in fatigue. When compressing the nerve roots of the spine with the spine, the pain can be more intense and is sharp. Its location in this case is not limited to the back area, but is felt by a person in the area of the limbs.
Phase of osteochondosis of the spine
The stage of the disease depends on the severity of the symptoms of osteochondosis of the spine. In the first phase of the osteochondosis of the spine, the pain is practically not felt, if only the light and weak stability of the spine for injuries. The destruction of the fibrous ring, a decrease in the size of the vertebral cracks and the pain of various intensity is a symptom of the osteochondosis of the spine of the second stage.
The third stage of the disease is characterized by significant deformations of the bone and vertebral tissue until the appearance of intervertebral hernias. The symptom of the osteochondrosis of the spine of the fourth stadium more serious are mass bone growth, limited mobility, intense pain and a complete or partial paralysis of the limbs caused by the compression of the nerve roots.
Symptoms of osteochondosis of the cervical column
The osteochondrosis of the cervical column often leads to blood circulation disorders due to the compression of the arteries. This leads to intense headache, dizziness and fainting. With the osteochondrosis of the cervical column, the vertebral artery syndrome is sometimes observed. It is characterized by a sense of noise in the head, the image of "flies" or colored spots in front of the eyes. With osteochondrosis of the cervical column, peripheral pains are also possible in the shoulders or hands.
Symptoms of osteochondosis of the thoracic spine
The osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine can aggravate the course of various heart diseases. The disease causes the progression of intercosphere neuralgia (intercostation nerves that holds). With the osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, the chest pain and the feeling of the "pole" in the center of the chest is observed.
Symptoms of osteochondosis of the lumbar column

The lumbar column osteochondrosis leads to the development of the following diseases: Lumbago and Hernia.
The Istia, as one of the complications of the osteochondosis of the lumbar column, is characterized by damage to the sciatic nerve, pain in the gluteal region, hypotension (reduced tone) of the calf and buttock muscles.
With a symptom of lumbago of osteochondosis of the lumbar column, there is severe pain in the lower back of the back, caused by a movement of the vertebrae or loss of the spinal disc.
Lumbar radicalitis, another complication of the lumbar column osteochondrosis, is caused by the hernias of the lowest discs of the spine. It is accompanied by pain in the buttocks with irradiation in the back of the thigh, a hole under the knee, a lower part of the leg and one foot.
Diagnosis of osteochondosis of the spine
The preliminary diagnosis of "osteochondosis of the spine" is established by the neurologist after the initial examination in relation to the patient's complaints on back pain and limited mobility. The stadium of the osteocondrosis of the spine is ascertained according to the degree of deformation of the spine, the patient's posture and the number of discs concerned.
All the aforementioned symptoms of the osteochondosis of the spine are diagnosed by feeling the patient's back. The doctor also pays attention to the state of muscle tone. Since in most cases the disease is accompanied by the hypertonicity of the back muscles.
Using the tests to bend the spine, the breadth of the patient's movements is determined. Thanks to the use of radiography, CT and magnetic resonance imaging, the diagnosis is specified and determined the future tactics of the treatment of the osteochondrosis of the spine.
Treatment of the osteochondrosis of the spine
In the treatment of osteochondosis of the spine, conservative and surgical methods are used. The goal of both is to eliminate pain syndrome and prevent further progression of the spinal deformation.
At the same time, the surgical treatment of spinal osteochondrosis is used only if the conservative therapy of the disease is ineffective.
The active stage of the application of conservative methods lasts on average 2 months. At the beginning of it, an short -term increase in pain syndrome caused by the reaction of the body to medicines, physiotherapy exercises (exercise therapy) and physiotherapy. In the conservative treatment of osteochondosis of the spine, massage, manual therapy, extract and reflexology are also used. The effectiveness of the treatment of osteochondosis of the spine depends on the systematic nature of the procedures and the perseverance of the patient himself in the execution of the operating therapy complexes.
The surgical treatment of the spinal osteocondrosis is carried out with an hernia of intervertebral discs, whose time ago exceeds 6 months. The indication for the operation is also a reduction in the gap between the 1/3 vertebrae of the initial size and the compression of the roots of the spinal cord.
The main method in the surgical treatment of the osteochondrosis of the spine is discouragement, that is, the removal of a deformed disc. The operation can be minimally invasive using endoscopic tools using the micro-desectomy method, the B-Bin system and the laser vaporization of the nucleus of a deformed disk.
After the surgical treatment of osteochondosis of the spine, a rehabilitation period is expected for 6 months. During it, the patient is aimed at treatment with Santorium-resort to undergo a physiotherapy course, manual therapy, acupuncture, etc.




















