Osteoarthritis is a pathological process of the joints that can have various causes.They all lead to disruption of the function and structure of one or more joints.This disease is the most common cause of chronic joint pain.It affects millions of people.In any case, the symptoms and treatment of arthrosis are individual and require observation by a qualified orthopedist.
What is osteoarthritis?
The basis of the disease is the progressive loss of cartilage, which normally covers the adjacent bone sections and ensures their mutual sliding.Under the influence of various reasons, the cartilage tissue begins to collapse, immature stem cells are activated in the underlying bone, it becomes denser, and cavities (cysts) and growths (osteophytes) form in it.
The space between the joint surfaces gradually narrows and then disappears completely and the limb stops moving.With osteoarthritis, all joint tissues are affected, including the surrounding muscles, ligaments and joint capsule.Therefore, treatment of joint arthrosis is a difficult task, and in the later stages only surgery can help the patient.
The most common form of the pathology is deforming arthrosis, which affects the large joints of the lower limbs and hands.
Causes of osteoarthritis
Possible reasons for the development of arthrosis:
- endocrine diseases - diabetes, hypothyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, acromegaly, obesity;
- injuries, both large (bone fractures, as a result of which their articular surfaces are displaced from the normal axis), and microscopic, but permanent (during hard work, constant professional or sports load);
- inflammatory processes: infectious arthritis, gout, rheumatoid diseases;
- metabolic disorders in the body: Paget's disease and Wilson-Konovalov's disease;
- congenital developmental anomalies, for example, different limb lengths;
- genetic defects in the structure of collagen, for example Ehlers-Danlos syndrome;
- neuropathies of various origins: diabetic, alcoholic;
- hemophilia with frequent hemorrhages in the joint cavity.
To successfully treat arthrosis of the joints it is necessary to eliminate the cause that caused it.
Symptoms and stages of osteoarthritis
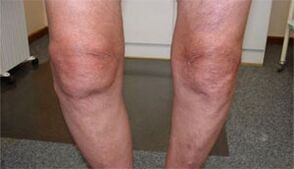
The disease is accompanied by the following disorders and external signs:
- aching pain and reduced mobility in one or more joints;
- painful sensations intensify after exercise, often at night, and in severe stages of arthrosis become permanent;
- a dangerous complication is joint immobility, the inability to move and take care of oneself.
Frequent forms of the disease:
- damage to the interphalangeal joints of the fingers and the base of the thumb, they can enlarge, swell, sometimes become painful, and inflammation develops in them;
- arthrosis of the hip joint: more common in men, associated with heavy physical work;the main cause of this disease in women is obesity;
- arthrosis of the knee joint: most often associated with professional activities in kneeling and squatting positions;
- arthrosis of the spine: accompanied by the formation of bone spurs that pinch the nerve roots, causing pain, weakness, reduced sensitivity of the limbs and constant pain in the lower back.
There are such degrees of arthrosis:
- 1st degree: slight limitation of mobility.
- 2nd degree: significant limitation of mobility, creaking during movements, moderate atrophy of nearby muscles.
- 3rd degree: deformation of the joint with almost total absence of movement inside it.
Depending on the degree of dysfunction and the stage of the pathology, doctors of various profiles - therapists, physiotherapists, rheumatologists, neurologists and orthopedists - are involved in the treatment of the disease.
Treatment of osteoarthritis
The goal of treatment is to eliminate risk factors and pain and restore joint function.For this, various methods of influence are used:
- non-pharmacological: patient information on his disease and prevention of complications, physiotherapy, weight loss, physiotherapy, use of aids (orthoses, canes, crutches);
- drugs for arthrosis: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, especially their new generation - selective COX-2 inhibitors;To relieve chronic pain, taking atypical antidepressants is indicated;slow-acting symptomatic drugs have only auxiliary value, since their effect in slowing down the destruction of cartilage has not been proven;
- with concomitant inflammation and severe pain, traumatologists perform intra-articular injections of glucocorticoid hormones;
- The most effective method is surgery, which allows you to eliminate pain and restore mobility.
Different types of surgery can be performed:
- arthroscopy: examination of the internal surface of the joint using a small video camera (endoscope), removal of cartilage fragments blocking the joint;
- arthroplasty – replacement of the cartilaginous surface with artificial material;
- osteotomy: cutting or removing part of the bone to restore the normal axis of the joint;
- arthroscopic surgery – surgical restoration of the integrity of the cartilage;
- arthrodesis – artificial creation of immobility in a joint (most often the ankle) to relieve the patient from constant pain;
- endoprosthesis: removal of damaged articular ends of bones and replacement with an artificial joint.
Prevention

There is no guaranteed way to prevent the disease.Prevention of arthrosis involves eliminating excessive load on the joints and timely treatment of diseases that contribute to the destruction of cartilage.Treatment of arthrosis with folk remedies does not slow down the progression of the disease, but helps to temporarily relieve joint pain.It can only be considered as an adjunct to traditional drug therapy or surgery.
Time is a negative factor for a patient with osteoarthritis.The sooner treatment or surgery is started, the better the results will be.Therefore, if symptoms of arthrosis appear, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor.




















